By Products |
Synchronisers and Load Sharing
|
|
Alarm Setter
Analog Panel Meter Battery Chargers Boiler Level Control Current & Power Guards & Controllers Dewpoint & Hygrometers Digital Panel Meter Digital Power/Multi-Function Meter Earth Fault Monitoring & Protection Fire Pump Controllers Frequency & Voltage Guards Gas Warning Systems Generator Protection & Controllers Industrial Communication & Converter Insulation Monitoring Jockey & Alarm Panels Level Control Loss of Mains Protection Measuring Transducers Meter Relay Power & Test Equipment Process Signal Transmitter Protector Trip Relay Shunts Switches Temperature Guards Transformers By Brands |
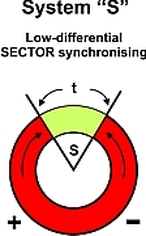
SYSTEM "S" - SECTOR SYNCHRONISATION
Bi-directional Check Synchronising Relay The system "S" guard is a low-differential Check Synchronising Relay. Synchronising relay closes when phase differential is within set limits (sector "S") for a pre-set time ("t"). Sector synchronisation is the classical alternative for applications which allows that synchronisation accuracy and speed of synchronisation are interrelated. Synchronisation accuracy (Df) can be calculated by following formula: Df = S : 360 x t i.e. set sector (S) to 10° and retention time (t) to 0.5 sec to obtain an accuracy (Df ) of 0.05 Hz. 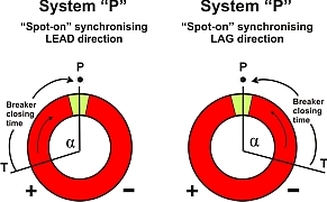
SYSTEM "P" - "SPOT-ON" SYNCHRONISATION
Uni-directional Fast and Accurate Synchronisation The dynamically controlled system "P" provides the fastest "spot-on" synchronisation. Dynamic breaker closing time compensation assures precision 12 o’clock synchronisation, when frequency of incoming generator is slightly higher than busbar frequency. Synchronising relay initiates generator breaker closure at moment "T", angle "a" is dynamically adjusted according the two systems frequency/phase differential. This directional synchronisation relay allows operation when frequency of incomer is HIGHER than bus frequency. In this way incomer is protected against motoric operation during start-up. To adapt the functionality of KSQ104F to any specific application, the direction of approach to synchronising (LEAD, LAG or NEUTRAL) can be selected as required:
LEAD is generally the preferred mode. The synchronising relay will then operate when the frequency of the incomer is slightly HIGHER than the bus frequency. This is to avoid motoring of the incomer (entering reverse power condition) after the breaker is closed. |